Number System
- VGC

- Jul 21, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jul 22, 2025
Types of Numbers Systems:

Natural Numbers (N): 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on ...

Useful to count number of items. Whole Numbers (W) : 0 and (N) : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on ...

In whole numbers, 0 is also considered along with all Natural numbers Integers (Z) : (W) and -ve of (N) : ... and so on -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on...

Rational Numbers (Q) : number that can be written in p/q form, where q ≠0. Example: 1/3, 14/16, and so on...

A thing divided into equal parts. Irrational Numbers (S) : number that cannot be written in p/q form, where q ≠0. : Example: √2, √3 and so on...

Real Numbers (R) : (Q) and (S)

Important Terms:
Co-prime numbers, also known as relatively prime or mutually prime numbers, are two or more integers that have no common factors other than 1. Example : 8/15, 4/15 and so on...
Equivalent rational numbers are different ways of representing the same value. Example 2/5=4/20=8/40 and so on... or 4/6 = 8/12 = 16/24 and so on...
Terminating fractions are those rational numbers whose decimal expansion terminates or ends after a finite number of steps. Example 7/8=0.875 or 1/2=0.5 or 639/250=2.556 and so on...
Non-Terminating recurring (repeating) fractions are those rational numbers whose decimal expansion do not terminates or ends after a finite number of steps. Example 1/3=0.333...= 0.‾3‾ or 1/7=0.142857142857142857...=0.‾142857‾ and so on.... These decimal expansion are written with the bar above the digits, indicating the block of digits that repeats.
Non-Terminating non-recurring (non-repeating) fractions are all irrational numbers whose decimal expansion do not terminates or ends after a finite number of steps and the sequence of numbers do not repeat even after many number of steps. Example √2=1.414213562... or √3=1.732050807... and so on....
Fundamentals :
Irrational numbers also satisfy the commutative, associative and distributive laws for addition and multiplication. However, the sum, difference, quotients and products of irrational numbers are not always irrational.
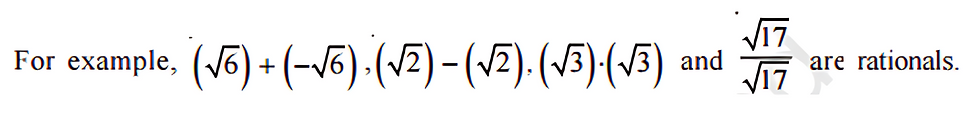



Techniques / Type of Questions:
True or False with reason.
Every whole number is a natural number. False, because zero is a whole number but not a natural number.
Every integer is a rational number. True, because every integer m can be expressed in the form m/1, and so it is a rational number.
Every rational number is an integer. False, because 3/5 is not an integer.
Find some rational or irrational numbers between two numbers.
Find five rational numbers between 1 and 2.
Since we want five numbers, we write 1 and 2 as rational numbers with denominator 5 + 1 i.e., 1 = 6/6 and 2 = 12/6.
So, the five numbers are 7/6, 8/6, 9/6, 10/6 and 11/6.
7/6 and 11/6 cannot be further reduced as 7 and 6 are co-prime numbers.
But, 8/6 can be further be reduced to 4/3; 9/6 can be reduced to 3/2; 10/6 can be reduced to 5/3.
So, final answer could be 7/6, 4/3, 3/2, 5/3 and 11/6.
Find five irrational numbers between 1 and 2.
Since we know irrational numbers are neither repeating nor terminating in decimal form, five irrational numbers between 1 and 2 can be:
1.1021..., 1.102101..., 1.102101002..., 1.1021010020003..., and 1.102101002000300004....
These numbers continue infinitely without repeating.
The three dots (...) indicate that the number is non-terminating, which is a necessary condition for a number to be irrational in decimal form.
Locate √x, where x = Natural number on number line. Example: locate √3 on number line.

Locate √x, where x = Positive decimal number on number line. Example: locate √3.5 on number line.

Take x + 1 units, here 3.5+1 cm, as diameter of the semicircle. Locate AB as x units (here 3.5 cm). Draw Perpendicular from B to the Semicircle. BD = √x
Find the decimal expansions of a fraction.
For Example decimal fraction of 10/3, 7/8 and 1/7

Fraction Form to Decimal Form by carrying out simple division of Numerator by Denominator Find the Rational number (p/q) expansions of a decimal number.
For Example find rational number of 0.875 , and 0.3333...

Addition , Subtraction , Multiplication and Division of Irrational Numbers
For example

Rationalize the denominator of irrational number.


Simplify irrational numbers with base and exponent
Example:



thanks